Home > Querying multiple endpoints
Support for the query of multiple endpoints
Use-case
Sometimes you don’t need to showcase a single knowledge graph, but rather multiple knowledge graphs. Sparnatural can act as a facade to query multiple SPARQL endpoints transparently for the user. Note that this imply that all SPARQL endpoints must share the same graph structure, as the same SPARQL query will be used to query them all.
How it works
- You need to create a JSON file giving the list of different endpoints that can be queried, with a few information about them (in particular their display labels). This JSON file is the endpoints catalog file.
- Sparnatural is configured with the URL of the different SPARQL services to query, and the JSON catalog file.
- When populating dropdown lists, or when querying for autocompletion values, Sparnatural will query all endpoints with which it is configured, and aggregate the results. In particular lists widgets will use an
optgroupseparator to separate the results of the different endpoints. - Call
sparnatural.executeSparql()with the final SPARQL query to have Sparnatural execute the query against all endpoints.
Configuring Sparnatural
To configure Sparnatural to query multiple endpoints, you need to:
- Provide a space-separated list of endpoints URL in the
endpointattribute of thespar-naturalelement. The URLs given here must correspond to theendpointURLof the catalog entries (see below) - Provide the URL of the catalog file to be loaded in the
catalogattribute of thespar-naturalHTML element. The catalog may contain more entries than the ones actually passed in theendpointattribute. - Deal yourself with the execution of the final query against the list of selected endpoints (see below)
Here is an example:
<!-- Note how 2 SPARQL endpoints URL are provided, along with the URL of the catalog file -->
<spar-natural
src="..."
endpoint="https://sage-ails.ails.ece.ntua.gr/api/content/rijksmuseum-poc/sparql https://sage-ails.ails.ece.ntua.gr/api/content/gooi-en-vecht-poc/sparql"
catalog="datasets.jsonld"
lang="en"
defaultLang="en"
distinct="true"
limit="1000"
debug="true"
></spar-natural>
JSON Catalog file
Catalog file example
Here is an example JSON catalog file :
{
"type": "Catalog",
"service": [
{
"id": "https://sparna-git.github.io/europeana-linkeddata-taskforce-poc/dataset/rijksmuseum",
"type": "DataService",
"title": {
"en" : "Rijksmuseum Collection"
},
"endpointURL" : "https://sage-ails.ails.ece.ntua.gr/api/content/rijksmuseum-poc/sparql",
"description": {
"en" : "Lorem ipsum..."
},
"extent": "statistics_rijksmuseum.ttl"
},
{
"id": "https://sparna-git.github.io/europeana-linkeddata-taskforce-poc/dataset/gooi-en-vecht",
"type": "DataService",
"title": {
"en" : "Gooi en Vecht Historisch"
},
"endpointURL" : "https://sage-ails.ails.ece.ntua.gr/api/content/gooi-en-vecht-poc/sparql",
"description": {
"en" : "Lorem ipsum..."
},
"extent": "statistics_gooi-en-vecht-poc.ttl"
},
{
"id": "https://sparna-git.github.io/europeana-linkeddata-taskforce-poc/dataset/gelderland",
"type": "DataService",
"title": {
"en" : "Collectie Gelderland"
},
"endpointURL" : "https://sage-ails.ails.ece.ntua.gr/api/content/gelderland-poc/sparql",
"description": {
"en" : "Lorem ipsum..."
},
"extent": "statistics_gelderland-poc.ttl"
}
]
}
Catalog file reference
The JSON catalog file is basically a DCAT description of the DataServices encoded in JSON-LD. DataServices are described with a few metadata. The root of the catalog file is the Catalog object.
Catalog entity
The Catalog object is the root entity of the file. It contains a service property that will contain all the DataServices entities:
"type": "Catalog",
"service": [
{
...
},
{
...
}
]
}
DataService entity
A DataService describes one endpoint to be queried. It contains:
- an
id, which is the internal identifier of this entry in the catalog - an
endpointURL, which is the URL of the SPARQL endpoint to which Sparnatural will send its queries - its
titles in different languages, which will be used when displaying this entry in the interface - optionaly, an
extentpointing to a statistics file of the dataset generated by the SHACL Play statistics analysis algorithm, that contains the statistics of the Dataset. Sparnatural uses the statistics to filter the properties and entities available to the user - other optional metadata, such as a
description, not used by Sparnatural but that can be useful to other parts of your application
{
"id": "https://sparna-git.github.io/europeana-linkeddata-taskforce-poc/dataset/gelderland",
"type": "DataService",
"title": {
"en" : "Collectie Gelderland"
},
"endpointURL" : "https://sage-ails.ails.ece.ntua.gr/api/content/gelderland-poc/sparql",
"description": {
"en" : "Lorem ipsum..."
}
}
Sparnatural behavior
When configured with more than one endpoint, Sparnatural will behave this way:
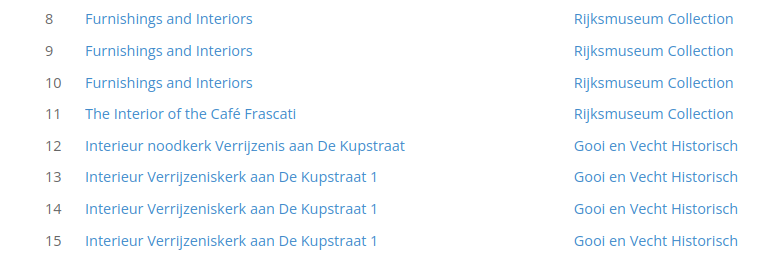
In lists, values are presented in a different section for each endpoint
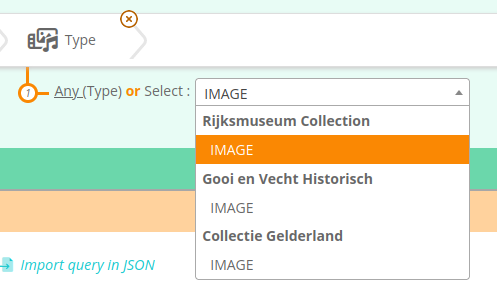
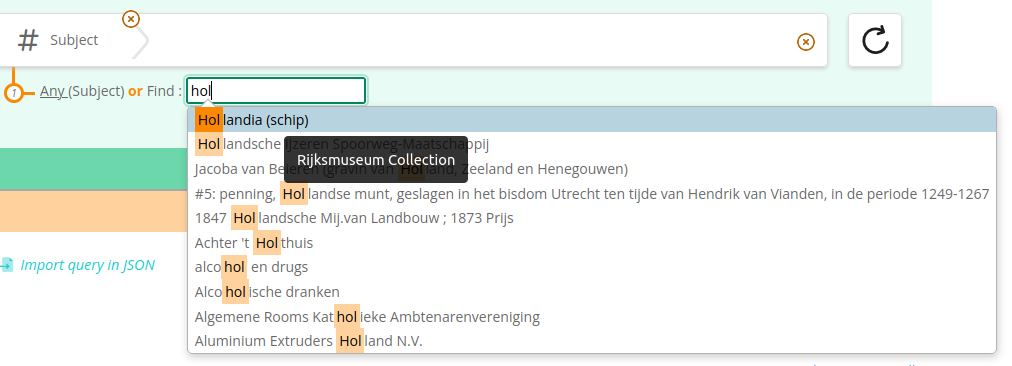
In autocomplete, endpoint is visible by hovering the result
Executing the final SPARQL query against all endpoints
Sparnatural can deal with the population of dropdown lists and autocomplete fields against multiple endpoints. You also need to execute the final query returned by Sparnatural against all endpoints. In order to do this you can call the executeSparql() method on Sparnatural, which will take care of:
- sending the SPARQL query to all endpoints in the catalog
- merging the results, adding an extra column for the source
- returning the merged result
The full integration looks like this:
sparnatural.addEventListener("queryUpdated", (event) => {
queryString = sparnatural.expandSparql(event.detail.queryString);
yasqe.setValue(queryString);
});
sparnatural.addEventListener("submit", (event) => {
// enable loader on button
sparnatural.disablePlayBtn() ;
let finalResult = sparnatural.executeSparql(
yasqe.getValue(),
(finalResult) => {
// send final result to YasR
yasr.setResponse(finalResult);
// re-enable submit button
sparnatural.enablePlayBtn();
},
(error) => {
console.error("Got an error when executing SPARQL in Sparnatural");
console.dir(error);
}
);
});
sparnatural.addEventListener("reset", (event) => {
yasqe.setValue("");
});
The source endpoint is added as an extra column: